Can Robots Truly Replicate Human Touch?
In March 2025, a team of surgeons in Zurich successfully repaired a congenital heart defect in a newborn in Nairobi—without leaving Switzerland. Guiding robotic arms through a telepresence haptic avatar, they felt the delicate pulse of the infant’s artery and adjusted their technique in real time. This milestone underscores the seismic shift driven by haptic technology, enabling remote physical interactions with unprecedented precision.
These avatars are not incremental advancements; they redefine how humans interact with physical environments remotely. By merging robotics, AI, and tactile actuators, telepresence haptic avatars address a critical void in remote collaboration: the absence of touch. For a deeper look at how robotics is transforming medical fields, explore the future of robotic surgery and its bold implications.
The Science Behind Telepresence Haptic Avatars
Telepresence haptic avatars rely on three core technologies:
- Tactile Sensors: Capture pressure, vibration, and temperature.
- Force Feedback Actuators: Replicate resistance (e.g., surgical scalpel meeting tissue).
- AI Synchronization: Compensate for latency and predict tactile responses.
A 2024 study by Stanford’s Haptics Lab revealed that users completing remote tasks with haptic technology showed 72% higher accuracy compared to visual-only systems. This precision is fueling innovations across industries, much like soft robotics artificial muscles that are transforming healthcare and space exploration.
Healthcare: Saving Lives Beyond Borders
Remote Surgery and Diagnostics
In 2023, Johns Hopkins researchers demonstrated the first transatlantic kidney biopsy using a telepresence haptic avatar. Surgeons in Baltimore detected malignant tissue in a patient in Lisbon by feeling the stiffness of cells—a tactile cue invisible on imaging scans. This breakthrough in remote surgery robots showcases how haptic technology transcends geographical barriers, much like AI-assisted artifact recovery systems preserving history.
Why Haptic Avatars Are Revolutionizing Surgery
The ability to feel tissue resistance through telepresence haptic avatars allows surgeons to perform complex procedures with confidence, even from thousands of miles away. Unlike traditional telemedicine, which relies on visuals, haptic systems provide tactile feedback critical for delicate operations like heart surgery. The Proprio Glove, an FDA-cleared haptic technology, exemplifies this, training surgeons in low-resource regions with 35% fewer errors by simulating incision depth and angle. This precision aligns with advancements in neural interface-controlled exoskeletons, which enhance physical capabilities in rehabilitation.
Real-World Example:
Proprio Glove: Used in 2024 to train surgeons in low-resource regions, this glove delivers real-time feedback, reducing errors by 35%.
“Haptics turn surgeons into remote extensions of their expertise. Feeling tissue resistance is non-negotiable in complex procedures.”
—Dr. Sarah Lim, Johns Hopkins Medical Robotics Division
Education: Democratizing Hands-On Learning
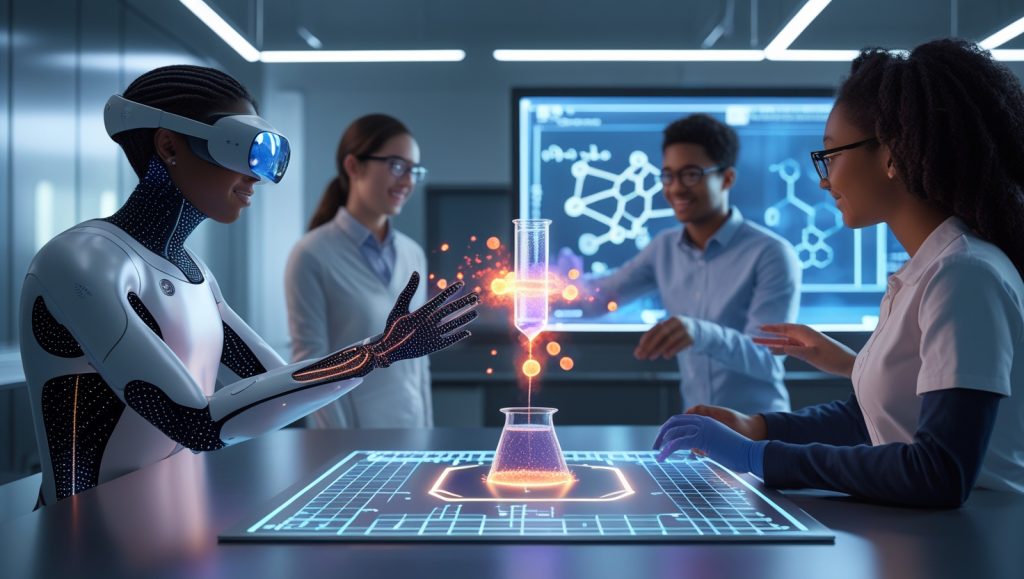

Virtual Laboratories
MIT’s 2024 pilot program equipped engineering students with telepresence haptic avatars to assemble microchips in VR. Participants reported a 40% faster learning curve compared to traditional methods, proving the value of virtual tactile systems. This mirrors how STEM robotics competitions are fueling innovation by providing hands-on learning experiences.
Why Haptic Avatars Enhance Learning Outcomes
Telepresence haptic avatars enable students to engage with physical simulations, from feeling the texture of materials to manipulating virtual objects. The Teslasuit, a wearable haptic technology used at Imperial College London, simulates chemical reactions, letting students experience heat from exothermic processes or the viscosity of liquids. This hands-on approach accelerates skill acquisition, similar to how robotics in 3D printing unlocks new educational possibilities.
Breakthrough:
Teslasuit: Students at Imperial College London use this system to feel chemical reactions, enhancing comprehension of complex concepts. For more on cutting-edge educational tech, visit Imperial College’s haptic chemistry lab.
Ethical and Technical Challenges
Privacy Risks in Haptic Data
Telepresence haptic avatars collect biometric data like grip strength and pulse, raising concerns about privacy. In 2024, the EU proposed the Haptic Data Protection Act to safeguard this data, addressing risks similar to those in AI-driven cybersecurity.
Why Data Security Is Critical for Haptic Systems
The sensitive nature of haptic data demands robust protection. Edge computing processes tactile data locally, minimizing cloud vulnerabilities and ensuring user trust. This approach aligns with efforts to secure AI-powered regtech solutions, which prioritize data integrity in high-stakes environments.
Solution:
Edge Computing: Process tactile data locally to minimize cloud vulnerabilities.
Latency: The 50ms Threshold
Even minor delays disrupt touch synchronization in telepresence haptic avatars. Companies like Ericsson and Qualcomm are optimizing 5G-Advanced networks to achieve sub-20ms latency, critical for seamless virtual tactile systems. Learn more about these advancements in Ericsson’s 5G-Advanced whitepaper.
Why Latency Remains a Barrier
Latency below 50ms is essential for real-time haptic feedback, yet current networks often fall short in remote regions. Overcoming this challenge will unlock the full potential of haptic technology, much like untethered deep-sea robots revolutionizing ocean exploration rely on robust connectivity.
The Future: Neurohaptics and Beyond
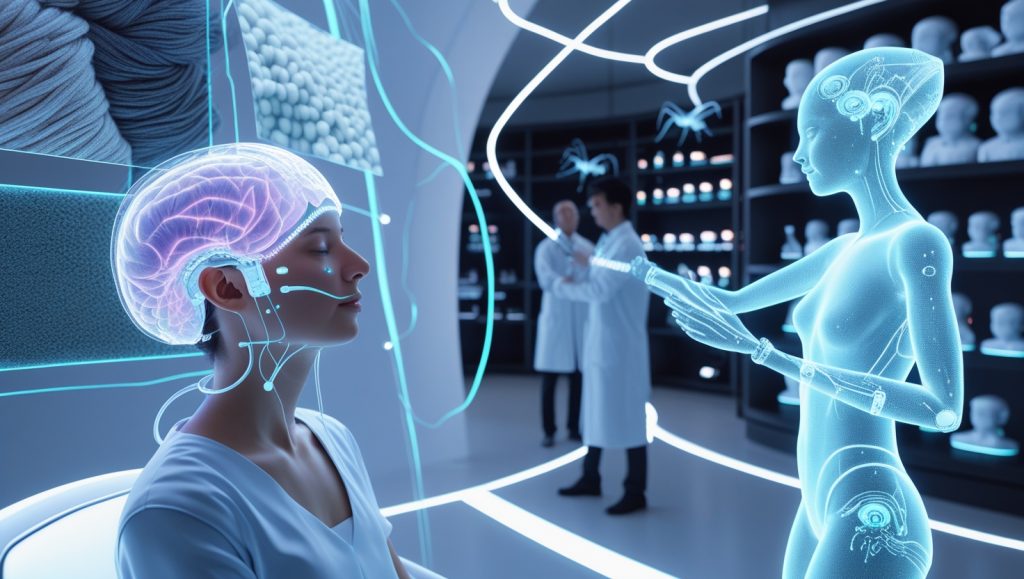

Direct Neural Interfaces
Neuralink’s 2024 trials showed that microelectrodes could restore touch in paralyzed patients, with 89% accuracy in distinguishing textures like wool and sandpaper. This leap in AI-driven haptics parallels biohybrid insect technology reshaping environmental innovation.
Why Neurohaptics Could Redefine Human Interaction
By bypassing damaged nerves, telepresence haptic avatars with neural interfaces could enable not just remote touch but also sensory restoration. Meta’s Haptic Metaverse, set for 2026, aims to integrate avatars that replicate handshakes and hugs, building on innovations like soft humanoid robots enhancing home safety.
Projected Innovation:
Meta’s Haptic Metaverse: By 2026, Horizon Worlds plans to integrate avatars with force feedback vests for immersive tactile experiences.
FAQ: Addressing Common Concerns
Are haptic avatars affordable for developing nations?
Current systems cost $10,000–$50,000, but nonprofits like Haptics for All aim to subsidize devices for rural hospitals by 2026
Can haptic gloves cause sensory overload?
Early models caused fatigue, but adaptive pressure algorithms now adjust feedback based on user sensitivity, ensuring comfort in virtual tactile systems.
How secure is haptic data transmission?
AES-256 encryption is standard, though ethical frameworks for data ownership remain in flux, a concern also raised in AI ethics debates.
The Unseen Bridge
Telepresence haptic avatars are not about replacing humans but amplifying their reach. From enabling surgeons to operate across oceans to letting students “touch” molecules, this haptic technology redefines accessibility. As latency shrinks and AI grows more intuitive, the line between physical and remote will blur—ushering in an era where touch knows no borders. For more on how robotics is reshaping industries, check out why robotics in recycling is transforming global sustainability.
Your Next Step?
Stay ahead of the curve. Subscribe to our newsletter for monthly deep dives into emerging tech.